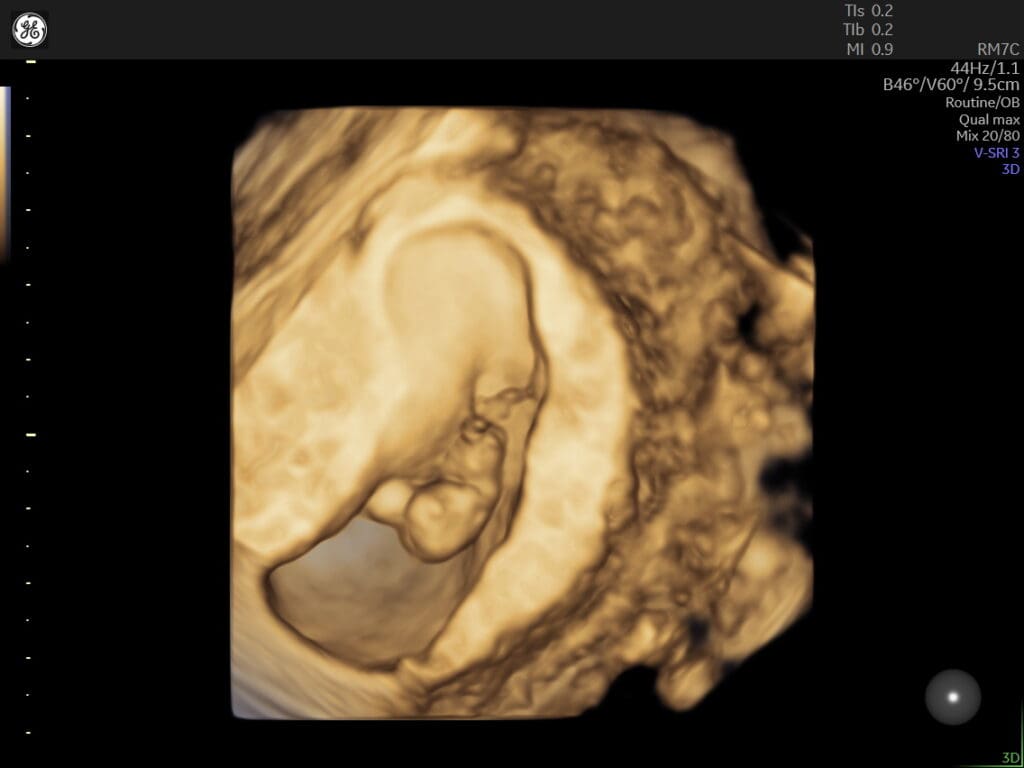
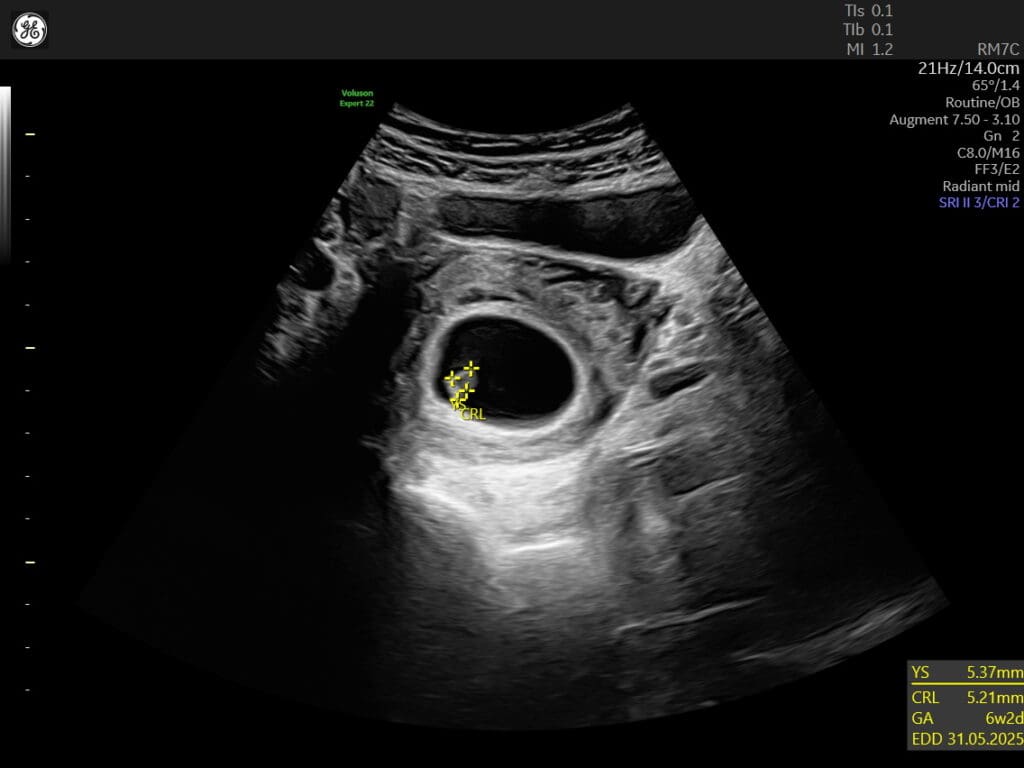
What is the Viability Scan?
The viability scan, also known as an early pregnancy scan, is a type of ultrasound examination performed during the first trimester of pregnancy. Its purpose is to assess the viability and health of the developing embryo or fetus.
The viability scan is usually conducted between 6 to 10 weeks of gestation. It aims to confirm the presence of a gestational sac, which is a fluid-filled structure where the baby develops, and to detect the baby’s heartbeat. This scan helps determine if the pregnancy is progressing as expected and if the baby is growing properly.
During the scan, a healthcare professional will use an ultrasound machine to carefully examine the uterus and the gestational sac. They will look for the presence of a yolk sac, which provides nourishment to the developing embryo, as well as the fetal pole, which contains the early stages of the baby’s body.
The detection of a heartbeat is a significant milestone in the viability scan. It indicates that the baby’s heart has started beating, which is a reassuring sign of a healthy pregnancy. Additionally, the scan may also provide an estimated gestational age, which helps in determining the due date and tracking the progress of the pregnancy.
The viability scan offers valuable information and peace of mind to expectant parents, especially if there were any concerns about the pregnancy. In cases where the scan raises any potential issues or if the pregnancy is deemed nonviable, further medical advice and support will be provided to the parents.
It’s important to note that the viability scan is a non-invasive and safe procedure. It allows healthcare professionals to assess the early stages of pregnancy and provide appropriate care and guidance to ensure the well-being of both the mother and the baby.